Wood is the primary material used in many construction projects. However, wooden structures are highly susceptible to heat and fire damage. That is why protective coatings on wood matter a lot. Many people now use heat-resistant paint for wood or fire-retardant paint to keep wooden surfaces safer. These paints provide protection and help reduce damage from heat and fire exposure.
Choosing the right paint improves safety and helps wooden structures last longer. Still, many homeowners and builders are unsure which product to use. Heat-resistant paint on wood works differently from fire-retardant paint. Each one serves a specific purpose. In this blog, we will discuss the major differences between these paints for wood to help you make an informed decision.
What Is Heat-Resistant Paint for Wood?
Heat-resistant paint for wood is used to handle high temperatures. It protects wooden surfaces exposed to high heat but not direct fire. This type of paint forms a layer that resists temperature damage and prevents surface cracking, peeling, or discoloration. People often use heat-resistant paint on wood near fireplaces, chimneys, stoves, grills, and kitchen areas.
It is also useful for wooden shelves near ovens and heating equipment. These paints usually withstand temperatures ranging from 200°C to 650°C, depending on the formula. This paint does not stop fire. Instead, it slows heat transfer. It protects the wood from thermal stress. Over time, constant heat can dry out wood and weaken its structure.
Heat-resistant paint helps prevent this by creating a barrier. Another benefit is improved durability. Wood coated with heat-resistant paint tends to last longer in hot environments. It also helps maintain appearance by reducing burn marks and color fading.
What Is Fire-Retardant Paint for Wood?
Fire-retardant paint works differently. Its main job is to slow down the spread of flames. When exposed to fire, it reacts chemically. It expands and forms a thick foam layer. This layer insulates the wood and limits oxygen exposure. This provides additional evacuation time during a fire emergency. It also helps reduce property damage. This makes it useful for homes, schools, offices, and public buildings. When fire touches the painted wood, the coating activates. It delays ignition and reduces flame spread.
The paint is water-based, non-toxic, and easy to apply with a sprayer, roller, or brush. Some products may not require a primer, depending on the substrate. This reduces time and cost. It also provides a smooth, clean finish, enhancing the appearance of wooden surfaces. With very low VOC levels, it meets strict safety standards, making it ideal for indoor use.
Some fire-retardant paints can prevent wood from catching fire for up to 30 to 120 minutes. This type of paint is not used to withstand constant heat. That makes it ideal for safety-focused applications. Fire-retardant paint is commonly used on wooden beams, ceilings, wall panels, staircases, doors, and decorative elements.
Many fire-retardant coatings also meet ASTM safety codes and building regulations, making them suitable for commercial spaces. They perform well on plywood, oriented strand board, Douglas fir, and other commonly used wood materials, making them versatile for commercial, residential, and industrial projects.
Note: To know more, click on “How to Apply Fire-Retardant Paint on Wood Properly”
Differences Between Fire-Retardant Paint and Heat-Resistant Paint for Wood
This table highlights the major differences between fire-retardant and heat-resistant paint when used on wood.
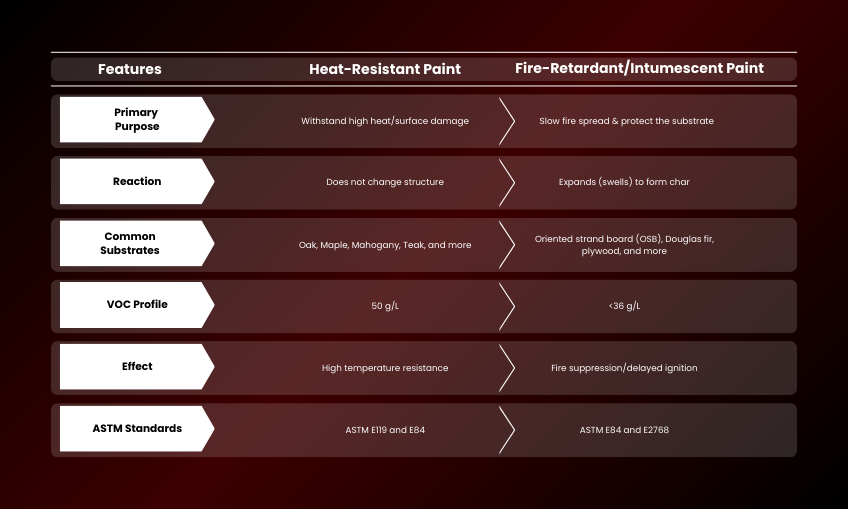
| Features | Heat-Resistant Paint | Fire-Retardant/Intumescent Paint |
| Primary Purpose | Withstand high heat/surface damage | Slow fire spread & protect the substrate |
| Reaction | Does not change structure | Expands (swells) to form char |
| Common Substrates | Oak, Maple, Mahogany, Teak, and more | Oriented strand board (OSB), Douglas fir, plywood, and more |
| VOC Profile | 50 g/L | <36 g/L |
| Effect | High temperature resistance | Fire suppression/delayed ignition |
| ASTM Standards | ASTM E119 and E84 | ASTM E84 and E2768 |
Heat-Resistant Paint vs. Fire-Retardant Paint: Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Many homeowners mistakenly assume both paints do the same job. This leads to wrong product selection.
- Another mistake is poor surface preparation when applying these paints. This reduces coating performance.
- Using low-quality paint can compromise safety and durability.
- Drying time varies for both. Skipping proper drying time also weakens fire protection.
- Following instructions carefully ensures optimal results.
Can You Use Both Paints on Wood?
In some cases, yes. But it requires careful product selection and professional advice. Some advanced coatings combine both heat resistance and fire-retardant properties. These are useful in high-risk zones such as kitchens in commercial buildings or industrial wood structures.
However, layering separate paints can lead to compatibility issues. You must check product guidelines before mixing these coatings. When you use both correctly, it can provide thermal stability and fire protection at the same time.
Final Thoughts on Fire-Retardant Paint vs. Heat-Resistant Paint for Wood
Wood remains a favorite building and design material. But safety must always come first. Understanding the difference between heat-resistant paint for wood and fire-retardant paint makes decision-making easier. Heat-resistant paint on wood protects against temperature stress. Fire-retardant paint protects against flames.
At Firefree Coatings, we provide advanced fire-retardant paint for wood used to deliver long-term performance. Our Firefree Class A fire-retardant paint for wood meets all ASTM E84 requirements and provides 30-minute extended protection. Our paint is listed by the California State Fire Marshal and inspected by the International Code Council. This ensures compliance with the highest fire safety standards. Contact us today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, fire-retardant and intumescent paints can be safely used on wood and timber structures to slow the spread of fire.
Yes, fire-retardant wood coatings should be ASTM tested to ensure they meet recognized safety and performance standards. ASTM testing verifies critical properties, including flame spread, smoke development, fire resistance, and durability.
Heat-resistant paint is used to withstand high temperatures, generally up to 600°C. This makes it ideal for surfaces exposed to intense heat but not direct flames.
Yes, when exposed to heat and flames, these coatings undergo a chemical transformation. They expand rapidly, sometimes up to 100 times their original thickness.


